About
Windows Embedded Compact, formerly Windows Embedded CE, Windows Powered and Windows CE, is an operating system subfamily developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows Embedded family of products.
Unlike Windows Embedded Standard, which is based on Windows NT, Windows Embedded Compact uses a different hybrid kernel. Microsoft licenses it to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), who can modify and create their own user interfaces and experiences, with Windows Embedded Compact providing the technical foundation to do so. The current version of Windows Embedded Compact supports x86 and ARM processors with board support package (BSP) directly. The MIPS and SHx architectures had support prior to version 7.0. 7.0 still works on MIPSII architecture.
Originally, Windows CE was designed for minimalistic and small computers. However CE had its own kernel whereas those such as Windows XP Embedded are based on NT. Windows CE was a modular/componentized operating system that served as the foundation of several classes of devices such as Handheld PC, Pocket PC, Auto PC, Windows Mobile, Windows Phone 7 and more.
Official mainstream support for the current and final version of Windows CE, Windows Embedded Compact 2013 ended on October 9, 2018, and extended support will end on October 10, 2023.
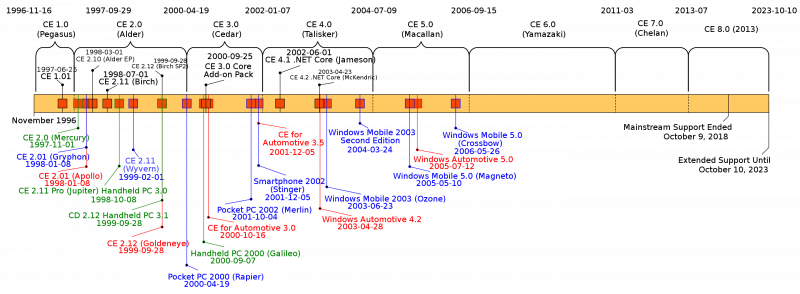
History
Windows Embedded Compact was formerly known as Windows CE. According to Microsoft, “CE” is not an explicit acronym for anything, although it implies a number of notions that Windows developers had in mind, such as “compact”, “connectable”, “compatible”, “companion” and “efficient”. The name changed once in 2006, with the release of Windows Embedded CE 6.0, and again in 2011, with the release of Windows Embedded Compact 7.
Windows CE was originally announced by Microsoft at the COMDEX expo in 1996 and was demonstrated on stage by Bill Gates and John McGill. Microsoft had been testing Pegasus in early 1995 and released a strict reference platform to several hardware partners. The devices had to have the following minimum hardware specifications:
- SH3, MIPS 3000 or MIPS 4000 CPU
- Minimum of 4 MB of ROM
- Minimum of 2 MB of RAM with a backup power source, such as a CR2032 coin cell battery
- Powered by two AA batteries
- A physical QWERTY keyboard including Ctrl, Alt and Shift keys
- An LCD display of 480×240 pixels with four shades of gray and two bits per pixel with touchscreen that could be operated by either stylus or finger
- An Infrared transceiver
- Serial port
- PC Card slot
- Built in speaker